The ongoing economic tensions between the US and China continues to create uncertainty for global traders. As major economic powers, their interactions are significantly influencing global markets, supply chains, and the broader economic environment.
Key Points
- The US imposed tariffs of up to 125% on Chinese goods, triggering sharp market reactions and retaliatory measures from China.
- Technology, EVs, agriculture, and consumer goods face rising costs and disrupted supply chains as trade tensions escalate.
- In these conditions, traders are considering strategies involving safe-haven assets, short-term trading, and long-term investments based on their individual risk tolerance and market analysis to manage risk.
Timeline of events and announcements
Here’s a timeline of key events between US and China since Trump’s second inauguration [1]:
11 April 2025
- Announced–China retaliates with higher tariffs: China raises tariffs on US goods to 125% from 12 April 2025, escalating a trade war that could disrupt global supply chains.
9 April 2025
- Announced–Trump decides 90-day pause on all tariffs, China not included: Only 13 hours after the tariffs were implemented, Trump decided to pause them for 90 days for more than 75 trading partners, with only the 10% baseline tariffs in place [2,3]. The only exception is China as Trump announced that he would increase reciprocal tariffs by 125%, in response to the former’s 84% retaliatory levies [4].
- Implemented–104% total tariffs on Chinese goods: The US formally enacted Trump’s steep tariff hike on Chinese imports, raising the total rate to an unprecedented 104%.
- Announced–China retaliates with 84% tariffs: Beijing announced retaliatory tariffs of 84% on US imports, responding to fresh US duties announced earlier in the day and further escalating tensions between the world’s two largest economies.
8 April 2025
- Announced–104% tariffs on China: In response to China’s 34% reciprocal tariffs, Trump announced plans to raise tariffs on China by an additional 50%, bringing the total tariff rate to 104% if China did not back down by 8 April [5].
5 April 2025
- Implemented–10% “Liberation Day” tariffs on imports over $800 USD: The US implemented the 10% universal tariff on imports above the $800 de minimis threshold, with exceptions for most USMCA goods and certain HS codes [6].
4 April 2025
- Announced–China’s 34% retaliatory tariffs on US goods: China announced 34% tariffs on all US goods, effective 10 April, along with export restrictions on rare earth elements and sanctions on 30 US defense organisations, escalating the trade conflict.
- Announced–Elimination of US de minimis exemption: Trump signed an executive order ending the $800 duty-free exemption for low-value shipments from China, Hong Kong, and Macau, effective 2 May.
2 April 2025
- Announced–“Liberation Day” 10% universal US tariff: Trump declared 2 April “Liberation Day” and announced a 10% baseline tariff on all imports, effective 5 April. China was served an additional 34% tariff, increasing its total rate to 54%. This marks the largest tariff increase since the 1930s.
4 March 2025
- Implemented–Tariffs on Chinese goods: The 20% tariff on Chinese goods are in effect.
3 March 2025
- Announced–20% tariff on Chinese goods: A new Executive Order raises tariffs on Chinese imports from 10% to 20%, effective 4 March, due to China’s inaction on the synthetic opioid supply chain.
2 March 2025
- Extended–De minimis exemption for Chinese goods: The US confirmed the $800 exemption will stay in place until CBP upgrades its systems to collect tariffs efficiently.
27 February 2025
- Announced–Additional 10% tariff on Chinese imports: Trump announced a second 10% hike on all Chinese goods, raising the total rate to 20% from 4 March.
10 February 2025
- Implemented–China retaliatory tariffs: China’s 10-15% tariffs on select U.S. goods took effect, covering crude oil, vehicles, agricultural machinery, coal, and LNG.
7 February 2025
- Reinstated–De minimis exemption for Chinese goods: The US temporarily restored the exemption for shipments under $800 until CBP updates its systems to manage tariff collection [7].
4 February 2025
- Implemented–10% tariff on Chinese imports: The previously announced 10% tariff took effect.
- Implemented–De minimis exemption removal for Chinese imports: Low-value shipments (under $800) from China are now subject to the 10% tariff, on top of existing duties from the first Trump administration.
- Announced–China’s retaliatory tariffs: China announced 10–15% tariffs on select US goods (effective 10 February) and filed a complaint with the World Trade Organization.
1 February 2025
- Announced–10% tariff on Chinese imports: Trump announces a 10% tariff on all Chinese imports, effective 4 February, citing concerns over China’s role on fentanyl control.
- Announced–De minimis exemption removal for low-value shipments of Chinese goods: Low-value shipments (under $800) from China and Hong Kong will now be taxed, ending the previous tariff exemption.
Recent US tariff measures
The US administration signalled a potential tariff increase on Chinese imports, possibly reaching 125% for specific categories. As of 9 April, the US has imposed a 104% tariff hike on Chinese goods.
Meanwhile, the US President has enacted a 90-day pause on tariffs for all other trading partners. Follow tariff updates here.
This action could potentially lead to increased prices for goods dependent on Chinese manufacturing, which may affect consumer prices. However, the extent of this impact is subject to various market dynamics.
Significant market shifts have already been observed. Apple (NASDAQ: APPL) experienced a 20% drop in its share price over the past month, the latest 90-day tariff pause caused the stock to jump by 15% on 10 April [8].
China’s retaliatory responses
In direct response to the US, China has imposed tit-for-tat retaliatory tariffs as high as 84% on US imports [9]. These actions extend beyond tariffs, including steps such as applying export controls on rare metals and probing US companies like Google and Nvidia with anti-monopoly inquiries [10].
Beyond immediate fiscal moves, China will not allow its yuan currency to depreciate sharply in order to make its exports cheaper and more attractive in global markets. Instead , state-linked enterprises have been strategically acquiring shares to help stabilise the financial market, signaling that Beijing is preparing for prolonged economic friction [11].
China has indicated it will continue to respond if US pressure persists. With new tariffs potentially targeting multiple Asian economies—analysts anticipate continued economic adjustment. Trading partners (excluding China) have been granted a 90-day reprieve, effective 9 April.
Read about how trading halted in asian markets.
Trade talks and diplomatic statements [12]
Trade talks between the US and China seem to have stalled. Tensions escalated after US Vice-President JD Vance made controversial remarks during a recent interview, prompting a response from Chinese foreign ministry spokesperson Lin Jian, who called them “ignorant and disrespectful” [13].
On 7 April 2025, President Trump threatened to impose an additional 50% levy on Chinese goods if Beijing did not withdraw its retaliatory tariffs. Senior advisors from think tanks like the China Center at The Conference Board have warned that any unilateral concession by China would weaken its negotiating position, potentially giving the US further leverage.
Experts suggest this situation could lead to long-term economic challenges. Global markets already show volatility—Asian shares dropped to historical lows before a significant rebound following Trump’s latest announcement of a 90-day tariff suspension.
Sectors most affected
The US and China are two of the largest trading partners in the world, with annual trade exceeding $500 billion [14].
China leads in US imports, especially electronics, machinery, and consumer goods, while the US supplies China with agricultural products, aircraft, and industrial machinery.
However, ongoing tariff escalations are putting a strain on this trade relationship, with far-reaching implications for various sectors.
Technology and semiconductors
Digital Trade and Supply Chains: The technology sector remains at the forefront of this trade conflict. With significant tariffs hitting electronics, including computers and smartphones, consumers face both immediate cost pressures and long-term supply chain uncertainties.
Apple, in particular, has been hit hard. Concerns over rising iPhone and Mac prices have intensified, resulting in long queues at US-based Apple Stores as consumers rush to buy products before potential price hikes take effect.
Semiconductor Challenges: The US has implemented measures to restrict China’s access to advanced microchips essential for artificial intelligence and other cutting-edge applications. These restrictions, in addition to potential future barriers, risk setting back China’s technological ambitions while prompting the US to look for alternative semiconductor partners.
Electric vehicles and batteries
Battery Production: Lithium-ion batteries, critical for electric vehicles (EVs), are among the goods heavily impacted by current tariffs. As these batteries become more expensive, the cost of EVs could also rise, influencing consumer adoption rates.
Strategic Resource Control: Both nations are leveraging tariffs and regulations to control the global supply of raw materials like lithium, which could influence the worldwide transition toward renewable energy and electric mobility.
Agriculture and commodities
US Agriculture Hits: On the export side, US agricultural products—most notably soybeans—have been targeted by Chinese retaliatory tariffs. Soybeans are vital for feeding China’s estimated 440 million pigs, and disruptions could impact food supply chains and prices internationally.
Commodities Under Pressure: The interconnected nature of US and Chinese commodity markets means that tariff escalations could disrupt global trade flows. With the US trade deficit with China at nearly $295 billion and agriculture playing a key role, farmers and commodities traders face an increasingly uncertain environment.
Consumer goods and retail
Everyday Products Affected: Consumer goods, including smartphones, toys, and video game consoles, are expected to see significant price increases due to rising tariffs. Smartphones, for example, make up about 9% of total US smartphone consumption from China, posing challenges for retailers in maintaining profit margins and managing consumer expectations.
Retail Market Volatility: The cascading effects of tariffs are not confined to technological or industrial products. Retailers, especially those heavily reliant on imported goods, may have to contend with supply disruptions, increased costs, and a challenging adjustment period as global supply chains realign.
Market reactions to US tariff implementation & subsequent 90-day pause
The implementation of the 125% US tariffs on Chinese goods sent ripples through global financial markets, leading to varied responses across major indices. The subsequent 90-day tariff pause announced by President Trump introduced additional dynamics, influencing market sentiments and movements.
Indices [15]
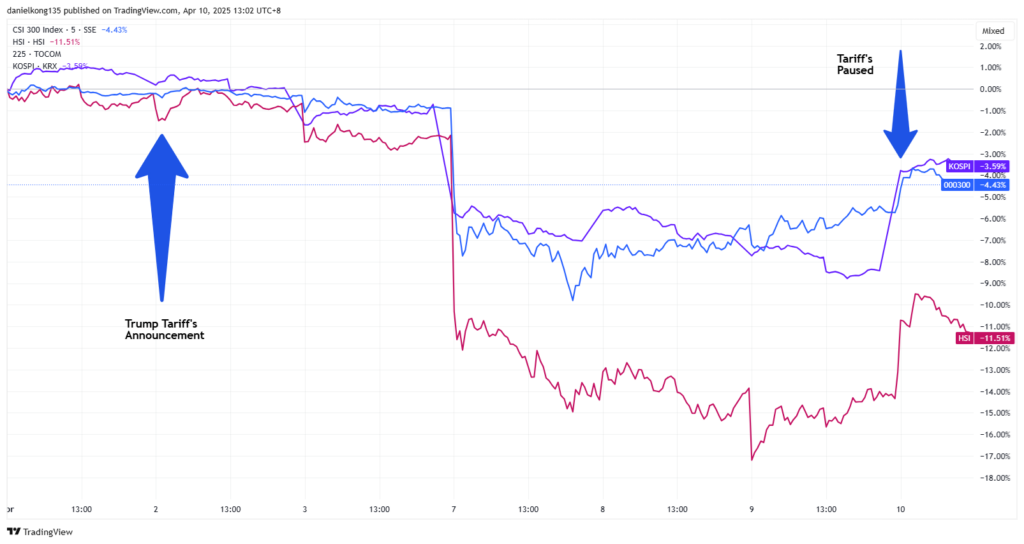
Chart 1: Chart for CSI 300, Nikkei 225, Hang Seng Index and Kospi from 1 April 2025 to 10 April 2025 (https://www.tradingview.com/x/b623J0B1/)
Following Trump’s announcement of a 90-day pause on tariffs on 9 April, Asian stock markets exhibited notable movements:
Prior to the 90-day pause:
- China’s CSI 300 Index: On 7 April, the index declined by 7%, reflecting investor concerns over escalating trade tensions.
- Hong Kong’s Hang Seng Index: The Hang Seng Index faced considerable pressure, dropping 8% on 7 April 7, marking its steepest decline since 1997.
- Japan’s Nikkei 225: The Nikkei 225 experienced significant volatility, slumping nearly 8% on Monday following the tariff implementation, its third-largest drop in history.
- South Korea’s Kospi Index: The Kospi Index also experienced a drop of 5.57% on 7 April, reflecting broader regional concerns.
After the 90-day pause:
- China’s CSI 300 Index: On 10 April, the CSI 300 Index rose by 0.99%, indicating a modest recovery.
- Hong Kong’s Hang Seng Index: The Hang Seng Index also increased by 1.8%, partially recovering from earlier losses.
- Japan’s Nikkei 225: On April 10, the Nikkei 225 surged by 8.45%, reflecting renewed investor optimism.
- South Korea’s Kospi Index: Similarly, the Kospi Index climbed by approximately 5%, indicating a positive market response.
Chinese Yuan
The Chinese yuan continued to weaken under the pressure of escalating trade tensions. On 9 April 2025, the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) set the daily reference rate at 7.2066 per dollar, the weakest level since September 2023 [16].
In response, the onshore yuan declined to 7.3499 per dollar, just shy of breaching the critical 7.3510 level, which marks its lowest point since late 2007 [17]. The yuan’s slide reflects growing market concerns over the economic fallout from the ongoing tariff war, which has triggered capital outflows and heightened volatility across Chinese financial markets.
Despite efforts by Chinese state banks to stabilise the currency—such as selling US dollars in the onshore market—the overall direction remains downward. Analysts say the controlled depreciation signals a strategic move by Beijing to offset the impact of US tariffs without sparking panic in the financial system.
With no signs of a policy reversal from the US, the yuan may face continued downward pressure given that China is exempted from the 90-day tariff pause, making it a key barometer for traders tracking the next phase of the trade war.
Chart 2: USD/JPY performance for the 6 months (https://www.tradingview.com/x/vHTLoCRj/ )
What traders should watch
Traders should closely monitor market volatility, especially in sectors heavily reliant on Chinese imports.
Upcoming policy announcements
- White House Briefings: Besides the latest 90-day tariff suspension, keep an eye on announcements from the White House regarding any adjustments or new tariffs.
- Trade Negotiations: While Trump has opened trade negotiations with South Korea, Japan, and other nations, China is not one of them. However, China remains open to negotiations with the world’s largest economy [18].
- Legislative Actions: Potential congressional actions that could impact tariff policies, such as bills requiring congressional approval for new tariffs.
Earnings reports from impacted sectors [19, 20, 21]
The escalating trade tensions between the US and China have had significant repercussions across earning reports from various industry sectors.
Technology: Companies like Apple may report significant impacts on earnings due to increased production costs.
Retail: Major retailers with supply chains linked to China could face higher production costs and reduced profit margins, leading to potential price increases for consumers.
Agriculture: US farmers are likely to report revenue losses due to China’s retaliatory tariffs on agricultural products, resulting in decreased exports and heightened uncertainty
Manufacturing: Higher tariffs on steel and aluminum equate higher production costs, possibly affecting profitability and competitiveness, particularly for automotive and construction manufacturers.
US-China summits and economic data releases [22]
China’s top leaders are expected to hold a high-level meeting this week to discuss measures to stabilise the economy and capital markets. Senior officials from various government and regulatory bodies will reportedly explore policies to boost domestic consumption, support markets, and potentially introduce export tax rebates.
The meeting reflects growing urgency in Beijing as it faces mounting economic pressure from escalating US trade actions.
Risk management in volatile conditions
In an increasingly volatile market, risk management is more crucial for traders and investors than ever.
Trading safe-haven assets
In times of elevated market volatility, traders often turn to traditional safe-haven assets.
Gold remains a key store of value during economic turbulence, with demand typically rising when geopolitical risks spike. Similarly, US Treasury bonds continue to attract inflows as investors seek security and capital preservation.
Incorporating these assets into your portfolio might help balance risk exposure during uncertain times influenced by the shifting US-China trade dynamics.
Opportunities in short-term vs long-term strategies
The current market environment presents opportunities for both short-term and long-term investment strategies.
Short-term traders may capitalise on rapid price movements in sectors directly affected by trade tensions, such as technology, commodities, and consumer goods. Conversely, long-term investors might identify opportunities in oversold equities or undervalued sectors with strong fundamentals.
Staying disciplined and aligning strategies with risk appetite is key, whether engaging in tactical trading or building a resilient, diversified portfolio for sustained growth.
Stay informed with Vantage
With the ongoing US-China trade conflict, keeping a close eye on policy shifts, market sentiment, and sector-specific developments is more important than ever. Whether you’re hedging risk or seeking new opportunities, having access to timely insights and reliable tools can give you a competitive edge.
Sign up for a Vantage account and explore our powerful trading tools and timely insights to stay ahead of global market shifts.
Reference
- “2025 U.S. tariffs – Zonos” https://zonos.com/docs/guides/2025-us-tariff-changes. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “What just happened? Making sense of Trump’s tariff pause – The Straits Times” https://www.straitstimes.com/business/economy/what-just-happened-making-sense-of-trumps-tariff-pause. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “Trump tariffs: ‘Do not retaliate and you will be rewarded,’ White House says – CNBC” https://www.cnbc.com/2025/04/09/trump-tariffs-live-updates.html. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “US pauses higher tariffs for most countries after market havoc, but hits China harder – BBC”. https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/c5y66qe404po. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- Trump Threatens to Slap an Additional 50% Tariff on China – The Wall Street Journal” https://www.wsj.com/livecoverage/stock-market-trump-tariffs-trade-war-04-07-25/card/trump-threatens-higher-tariffs-on-china-in-new-social-media-post-FBdyJkNi4IjF8qmBtx59?. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “What’s in Trump’s sweeping new reciprocal tariff regime – Reuters” https://www.reuters.com/world/us/whats-trumps-sweeping-new-reciprocal-tariff-regime-2025-04-03/. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “Trump pauses de minimis repeal as packages pile up at US customs – Reuters” https://www.reuters.com/business/trump-signs-order-delaying-tariffs-de-minimis-imports-china-2025-02-07/. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “Apple Inc. – MarketWatch” https://www.marketwatch.com/investing/stock/aapl. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “China slaps 84% retaliatory tariffs on U.S. goods in response to Trump – CNBC” https://www.cnbc.com/2025/04/09/china-slaps-retaliatory-tariffs-of-84percent-on-us-goods-in-response-to-trump.html. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “China announces measures against Google, other US firms, as trade tensions escalate – Reuters” https://www.reuters.com/technology/china-anti-monopoly-regulator-launches-probe-into-google-2025-02-04/. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “Exclusive: China’s central bank asks state lenders to reduce dollar purchases, sources say – Reuters” https://www.reuters.com/world/china/chinas-central-bank-asks-state-lenders-reduce-dollar-purchases-sources-say-2025-04-09/. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “China is not backing down from Trump’s tariff war. What next? – BBC” https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/ckg51yw700lo. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “Beijing attacks JD Vance’s ‘Chinese peasants’ remark in tariffs interview – The Guardian” https://www.theguardian.com/world/2025/apr/08/beijing-attacks-jd-vances-chinese-peasants-remark-in-tariffs-interview. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “Total value of U.S. trade in goods (export and import) with China from 2014 to 2024 – Statista” https://www.statista.com/statistics/277679/total-value-of-us-trade-in-goods-with-china-since-2006/. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “Hang Seng Index sidesteps bear trap as Trump’s tariff kick-off mauls Asia-Pacific markets – South China Morning Post” https://www.scmp.com/business/china-business/article/3305755/hong-kong-stocks-fall-following-rebound-us-tariffs-china-loom-large?module=latest&pgtype=homepage. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “Beijing signals determination to defend currency after offshore yuan tumbles to record low – South China Morning Post” https://www.scmp.com/economy/china-economy/article/3305751/offshore-yuan-hits-record-low-us-readies-additional-50-tariffs-imports-china. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “Yuan falls to 2007 lows as US tariffs on China kick in – Reuters” https://www.reuters.com/markets/currencies/yuan-falls-2007-lows-us-tariffs-china-kick-2025-04-09/. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “The United States and China are locked in a faceoff over tariffs. No one wants to blink first – ABC News” https://abcnews.go.com/US/wireStory/united-states-china-locked-faceoff-tariffs-blink-120656265. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “Tariff-related iPhone price increases estimated to be lower than feared – AI” https://appleinsider.com/articles/25/04/07/new-post-tariff-iphone-cost-estimate-comes-in-much-lower-at-just-29-more. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “Trump’s Tariffs Disrupt Global Sportswear; Shenzhou, Amer, and Asics Face Earnings Pressure – Morningstar” https://www.morningstar.com/company-reports/1272780-trumps-tariffs-disrupt-global-sportswear-shenzhou-amer-and-asics-face-earnings-pressure. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “Trump Tariff: Sectors That Are Worst Hit – Analytics Insight” https://www.analyticsinsight.net/photo/trump-tariff-sectors-that-are-worst-hit. Accessed 10 April 2025.
- “Exclusive-China to hold high-level meeting in response to US tariffs, say sources – MSN” https://www.msn.com/en-ca/money/general/exclusive-china-to-hold-high-level-meeting-in-response-to-us-tariffs-say-sources/ar-AA1CzPoZ. Accessed 10 April 2025.



